NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science chapter 6 Life Processes: The chapter teach you Life Processes of all living organisms, There are six life processes i.e movement, respiration, growth, reproduction, excretion and nutrition. The topic included in thi chapter are
- Life Processes
- What Are Life Processes?
- Nutrition
- Respiration
- Transportation
- Excretion
Students who are preparing for their Class 10 exams and searching for chapter-wise NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science must go through NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes.
ALSO CHECK – NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
ALSO CHECK – Download the free Class 10th Notes here
These NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes is prepared by our best subject experts teachers group thats help students to understand all the topics easily. With the help of these NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science, students can understand the complex topics of class 10 science. We all know Science is a subject that needs a clear understanding of the concepts and topics to score well in it.
ALSO READ – Top 5 best laptop under 50000 for students and office uses in In
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Intext Questions
Page Number: 95
Question 1
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans ?
Answer:
In multicellular organisms like humans, all the body cells are not in direct contact with the surrounding environment. Therefore, every cell of the body will not get oxygen as per need by the process of diffusion from the environment. Therefore diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms.
Question 2
What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive ?
Answer:
Walking, breathing, growth and other visible changes can be used to determine whether something is alive or dead. However some living things will have changes that are not visible to our eye; Hence, presence of life process is a fundamental criteria to decide whether something is alive.
Question 3
What are outside raw materials used by an organism ?
Answer:
Outside raw material is used by organism for food and oxygen. Raw materials requirement varies on the complexity of the organism and the environment it is living.
Question 4
What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life ?
Answer:
Processes essential for maintaining life are :
(i) Nutrition
(ii) Respiration
(iii) Transportation
(iv) Excretion
Page Number: 101
Question 1
What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition ?
Answer:
| Autotrophic nutrition | Heterotrophic nutrition |
| (i) In this mode of nutrition an organism makes or synthesizes its own food. | (i) In this mode of nutrition an organism cannot make or synthesize its own food |
| Organisms use simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water and synthesise their food in presence of sunlight. | (ii) Organisms cannot make their own food from simple inorganic matter and depend on other organisms for their food. |
| (iii) All green plants and some algae undergo this mode of nutrition. | (iii) All the animals, most bacteria and fungi undergo this mode of nutrition. |
Question 2
Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis ?
Answer:
(i) Carbon dioxide : Plants get carbon dioxide from the environment/atmosphere through stomata.
(ii) Water : Plants absorb water from the soil through roots and transport to leaves.
(iii) Sunlight : Plants get sunlight from the sun.
(iv) Chlorophyll : It is present in chloroplast found in green leaves and green parts of plants.
Question 3
What is the role of the acid in our stomach ?
Answer:
HCl present in the stomach dissolves food particles and creates an acidic medium. In acidic environment protein digesting enzymes pepsinogen is converted into pepsin. HCl in the stomach also acts as protective barrier against many disease causing pathogens.
Question 4
What is the function of digestive enzymes ?
Answer:
The food we eat is complex in nature, i.e., it contains complex molecules. Digestive enzymes break down these complex molecules into smaller simpler molecules so that they can be absorbed by the walls of the intestine.
Question 5
How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food ?
Answer:
The small intestine is designed to provide maximum area for absorption of digested food and its transfer into the blood for its circulation into the body. For this the inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body.
Page Number: 105
Question 1
What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration ?
Answer:
Aquatic organisms use oxygen dissolved in surrounding water. Since air dissolved in water has fairly low concentration of oxygen, the aquatic organisms have much faster rate of breathing.
Terrestrial organisms take oxygen from the oxygen-rich atmosphere through respiratory organs. Hence, they have much less breathing rate than aquatic organisms.
Question 2
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms ?
Answer:
First step of breakdown of glucose (6 carbon molecules) takes place in the cytoplasm of cells of all organisms. This process yields a three carbon molecule compound called pyruvate.
Further break down of pyruvate takes place in different ways in different organisms.
(i) Anaerobic respiration : The anaerobic respiration in plants (like yeast) produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as end products.
(ii) Aerobic respiration : In aerobic respiration break down of pyruvate takes place in presence of oxygen to give rise three molecules of carbon dioxide and water. The release of energy in aerobic respiration is much more than in anaerobic respiration.
(iii) Lack of oxygen : Sometimes, when there is lack of oxygen especially during physical exercise, in our muscles, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid (3 carbon molecule compound). Formation of lactic acid in muscles causes cramp.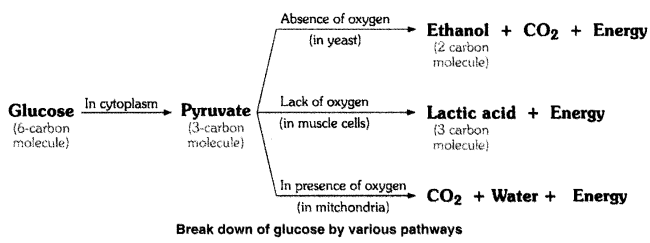
Question 3
How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings ?
Answer:
(i) Transport of oxygen : Haemoglobin present in the blood takes up the oxygen from the air in the lungs. It carries the oxygen to tissues which are deficient in oxygen before releasing it.
(ii) Transport of carbon dioxide : Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. Therefore, it is mostly transported from body tissues in the dissolved form in our blood plasma to lungs. Here it diffuses from blood to air in the lungs.
Question 4
How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases ?
Answer:
Within the lungs, the air passage divides into smaller and smaller tubes, called bronchi which in turn form bronchioles. The bronchioles terminate in balloon-like structures, called alveoli. The alveoli present in the lungs provide maximum surface for exchange of gases. The alveoli have vary thin walls and contain an extensive network of blood vessels to facilitate exchange of gases.
Page Number: 110
Question 1
What are the components of the transport system in human beings ? What are the functions of these components ?
Answer:
The transport system (circulatory system) in human beings mainly consists of heart, blood and blood vessels.
(i) Function of heart : The heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body parts and pumps it to lungs for enriching with oxygen. It receives purified blood from lungs and pumps it around the body.
(ii) Function of blood : Blood transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, digested food, hormones and nitrogeneous waste like urea. It also protects the body from diseases and regulates the body temperature.
(iii) Function of blood vessels : The blood pushed by the heart flows through the blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) and also comes back to the heart through them.
Question 2
Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds ?
Answer:
Separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood allows good supply of oxygen to the body. This system is useful in animals that have high energy requirement. Mammals and birds constantly need oxygen to get energy to maintain their body temperature constant.
Question 3
What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
Answer:
In highly organised plants there are two conducting tissues xylem and phloem.
Xylem consists of vessels, tracheids and other xylem tissues. The interconnected vessels and tracheids form a continuous system of water conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant. Xylem carries water and minerals.
Phloem conducts soluble products of photosynthesis from leaves to different parts of the plant body.
Question 4
How are water and minerals transport in plants ? [AICBSE 2015]
Answer:
The roots of a plant have hair called root hair.
The root hair are directly in contact with the film of water in between the soil particles. Water and dissolved minerals get into the root hair by the process of diffusion. The water and minerals absorbed by the root hair from the soil pass from cell to cell by osmosis through the epidermis, root cortex, endodermis and reach the root xylem.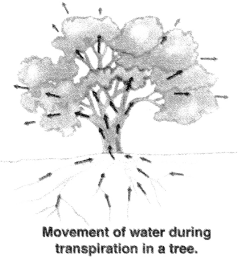
The xylem vessels of the root of the plant are connected to the xylem vessels of its stem.
Therefore the water containing dissolved minerals enters the root xylem vessels into stem xylem vessels. The xylem vessels of the stem branch into the leaves of the plants. So, the water and minerals carried by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves through the branched xylem vessels which enter from the petiole (stalk of the leaf) into each and every part of the leaf. Thus the water and minerals from the soil reach through the root and stem to the leaves of the plants. Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a suction which pulls water from the xylem cells of roots. The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is known as transpiration.
Question 5
How is food transported in plants ?
Answer:
Food is transported in plants by a special organ called as phloem. Phloem transports food materials from leaf to different parts of a plant. Transportation of food in phloem is achieved by the expenditure of energy from ATP. This increases osmotic pressure in the tissue causing water to move. This pressure moves material in the Phloem to the tissues with less pressure. This is helping in transportation of food material as per the needs. Ex: Sucrose
Page Number: 112
Question 1
Describe the structure and functions of nephrons.
Answer:
Structure of nephron : Each nephron is composed of two parts. First one is a cup-shaped bag at its upper end which is called Bowman’s capsule.
The Bowman’s capsule contains a bundle of blood capillaries which is called glomerulus. One end of the glomerulus is attached to the renal artery which brings the impure blood containing the urea waste into it. These impurities are filtered. The other part of the nephron is coiled. In this part, the substances like sugar (glucose), amino acid, ions and excess water which are required by the body, are reabsorbed. The substance remained in the nephron is mainly urine containing dissolved urea in water which is expelled from the body through urethra from time to time.
Main components of Nephrons are
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Long renal Tube
Structure of Nephron

Functions of nephron : Filtration of blood takes place in Bowman’s capsule from the capillaries of glomerulus. The filtrate passes into the tubular part of the nephron. This filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, salts and water.
Reabsorption : As the filtrate flows along the tubule, useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts and water are selectively reabsorbed into the blood by capillaries surrounding the nephron tubule.
Urine : The filtrate which remained after reabsorption is called urine. Urine contains dissolved nitrogenous waste like urea and uric acid, excess salts and water. Urine is collected from nephrons to carry it to the ureter from where it passes into urinary bladder.
Question 2
What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products ?
Answer:
(i) The plants get rid of gaseous products-through stomata in leaves and lenticels in stems.
(ii) The plants get rid of stored solid and liquid waste by the shedding off leaves, peeling off bark and felling off fruits.
(iii) The plants get rid of wastes by secreting them in the form of gums and resins.
(iv) Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Question 3
How is the amount of urine produced regulated ?
Answer:
The amount of urine is regulated by kidney. It depends on the quantity of excess water and wastes dissolved in water.
(i) Quantity of water : When water is abundant in the body tissues, large quantities of dilute urine is excreted out. When water is less in quantity in the body tissues, a small quantity of concentrate urine is excreted.
(ii) Quantity of dissolved wastes : Dissolved wastes, especially nitrogenous wastes, like urea and uric acid and salts are excreted from the body. When there is more quantity of dissolved wastes in the body, more quantity of water is required to excrete them. Therefore, the amount of urine produced increases.
(iii) Hormones : The amount of urine produced is also regulated by certain hormones which control the movement of water and Na+ ions in and out of the nephrons.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(i) nutrition
(ii) respiration
(iii) excretion
(iv) transportation
Answer:
(iii) Excretion
Question 2
The xylem in plants are responsible for
(i) transport of water
(ii) transport of food
(iii) transport of amino acids
(iv) transport of oxygen
Answer:
(i) Transport of water
Question 3
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(i) carbon dioxide and water
(ii) chlorophyll
(iii) sunlight
(iv) all of the above
Answer:
(iv) All of the above
Question 4
The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(i) cytoplasm
(ii) mitochondria
(iii) chloroplast
(iv) nucleus
Answer:
(ii) Mitochondria
Question 5
How are fats digested in our bodies ? Where does this process take place ?
Answer:
Digestion of fats takes place in the small intestine.
Bile juice secreted by the liver poured in the intestine along with pancreatic juice. The bile salts present in the bile juice emulsify fhe large globules of fats. Therefore, by enulsification large globules break down into fine globules to provide larger surface area to act upon by the enzymes.
Lipase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice causes break down of emulsified fats. Glands present in the wall of small intestine secrete intestinal juice which contains lipase enzyme that converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.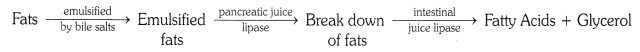
Question 6
What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food ?
Answer:
Saliva contains salivary amylase enzyme that breaks down starch into sugars like maltose.![]()
Saliva keeps the mouth cavity clean and moistens the food that help in chewing and breaking down the big pieces of food into smaller ones.
Question 7
What are the necessary conditions (or autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products ?
Answer:
Necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition :
- The energy and carbon requirements of the autotrophic organism is obtained by the process of photosynthesis.
- It is defined as the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside surroundings and convert them into stored forms of energy.
- This substance is taken in the form of carbon dioxide and water, which is converted into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
- The main purpose of carbohydrates is to provide energy to the plant. The carbohydrates are not utilized immediately; but they are stored in the form of starch, which serves as an internal energy reserve.
- The stored energy can be used as and when required by the plant.
Question 8
What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration ? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer:
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| 1. It takes place in the presence of oxygen. | 1. It takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| 2. Complete breakdown of food occurs in aerobic respiration. | 2. Partial breakdown of food occurs in anaerobic respiration. |
| 3. The end products in aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water. | 3. The end products in anaerobic respiration may be ethanol and carbon dioxide (as in yeast plants) or lactic acid (as in animal muscles). |
| 4. Aerobic respiration produces a considerable amount of energy. | 4. Much less energy is produced in anaerobic respiration. |
Some organisms which use anaerobic respiration are yeast, bacteria etc.
Question 9
How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases ?
Answer:
- The lung is an important part of the body. The passage inside the lungs divides into smaller and smaller tubes, which finally terminate in balloon-like structures, called as alveoli.
- The alveoli provide a surface where the exchange of gases can take place. The walls of the alveoli usually contains an extensive network of blood vessels. We know that, when we breathe in, we lift our ribs, flatten our diaphragm and chest cavity becomes larger.
- Because of this action, air is sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli.
- The blood brings the essential carbon dioxide from rest of the body and supply it to alveoli; the oxygen in the alveolar air is taken up by the blood in the alveolar blood vessels to be transported to the all other cells of the body. During normal breathing cycle, when air is taken in and let out, the lungs always contain a residual volume of air so that there is sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and carbon dioxide to be released.
Question 10
What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer:
Due to the deficiency of haemoglobin in blood, its oxygen carrying capacity decreases. As a result the production of energy by oxidation will become slower. Therefore, one would fall sick and would feel fatigue most of the time.
Question 11
Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary ?
Answer:
In our heart blood enters twice and also pumped out twice from the heart. The deoxygenated blood from the body is brought to the right atrium through vena cava from where it is sent to right ventricle. From right ventricle, the blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation through pulmonary artery. The oxygenated blood from lungs again enters the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins. From left atrium it is send to left ventricle, from where this oxygenated blood is pumped to different parts of body through the arteries. In this way the blood flows through the heart twice, that’s why it is called ‘double circulation’.
Necessity of double circulation: The right side and the left side of the human heart are useful to keep deoxygenated and oxygenated blood from mixing. This type of separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood ensures a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in case of humans who constantly need energy to maintain their body temperature.
Question 12
What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem ?
Answer:
| Xylem | Phloem |
| 1. Xylem conducts water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves and other parts. | 1. Phloem conducts prepared food material from leaves to other parts of plant in dissolved form. |
| 2. In xylem, the transport of material takes place through vessels and tracheids which are dead tissues. | 2. In phloem, transport of material takes place through sieve tubes with the help of companion cells, which are living cells. |
| 3. In xylem upward movement of water and dissolved minerals is mainly achieved by transpiration pull. It is caused due to suction created by evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf. | 3. In translocation, material is transferred into phloem tissue using energy from ATP. This increases the osmotic pressure that moves the material in the phloem to tissues which have less pressure |
Question 13
Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Answer:
| Alveoli | Nephron |
| 1. Alveoli are functional unit of lungs. | 1. Nephrons are functional unit of kidney. |
| 2. A mature lung has about 30 crore alveoli. | 2. A kidney has about 10 lakh nephrons. |
| 3. Alveoli provide a wide surface for gaseous exchange. | 3. The surface area of a nephron is not much more. |
| 4. The exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place through the network of capillaries in alveoli. | 4. The Bowman’s capsule in nephron regulates the concentration of water and salts. |







