NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Updated for 2022-23
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds is about compounds and their properties. We learn about chemical properties of carbon and its compounds such as combustion, oxidation, addition reaction, substitution reaction. Students who are preparing for their Class 10 exams and searching for chapter-wise NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science must go through NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds.
ALSO CHECK – NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 is prepared by our best subject experts teachers group thats help students to understand all the topics easily. With the help of these NCERT Solutions for Science, students can understand the complex topics of class 10 science. We all know Science is a subject that needs a clear understanding of the concepts and topics to score well in it.
ALSO READ – Top 5 best laptop under 50000 for students and office uses in India 2022
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds – In-text Questions
Page Number: 61
Question 1
What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2 ?
Answer: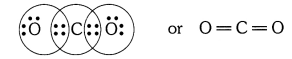
Question 2
What would be electron dot structure of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur.
Answer: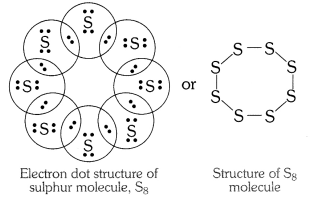
In-text questions set 2 Page Number: 68 – 69
Question 1
How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane ?
Answer:
Three, these are n-pentane, iso-pentane and neo-pentane.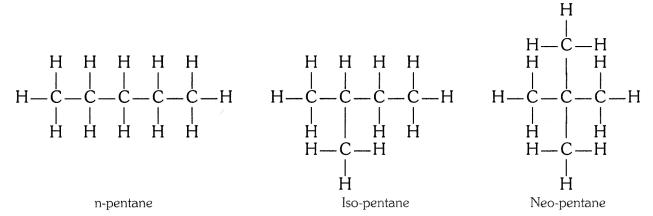
Question 2
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us ?
Answer:
(i) Tetravalency
(ii) Catenation.
Question 3
What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane ?
Answer:
The molecular formula of cyclopentane is C5 H10 .
The electron dot structure of cyclopentane is given on the next page.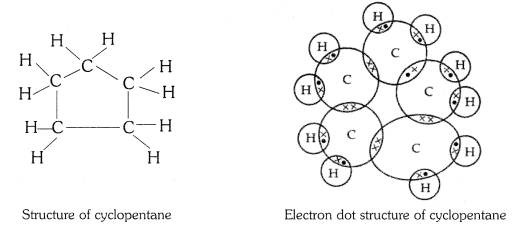
Question 4
Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Answer:
(i) Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)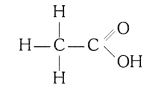
(ii) Bromopentane (C5H11Br)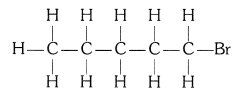
(iii) Butanone (CH3 — CH2 — COCH3)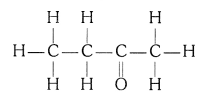
(iv) Hexanal (C5H11CHO)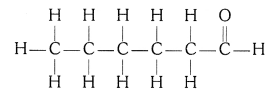
Structural isomers for bromopentane: There are three structural isomers for bromopentane depending on the position of Br at carbon 1, 2, 3.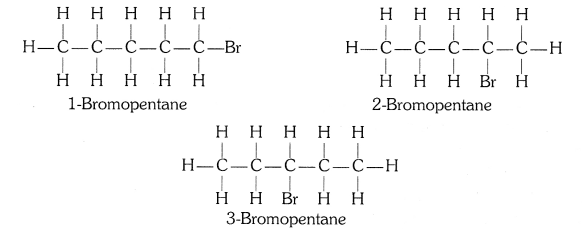
Positions 4 and 5 are same as 1, 2.
Question 5
How would you name the following compounds ?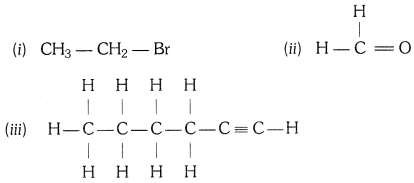
Answer:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal or Formaldehyde
(iii) 1 – Hexyne
In-text questions set 3 Page Number: 71
Question 1
Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction ?
Answer:
Conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction because addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation. Here, oxygen is added to ethanol by oxidising agent like alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate and it is converted into acid.
Question 2
A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used ?
Answer:
A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding instead of mixture of ethyne and air because the production of heat is very important for welding metals. When oxygen and ethyne are burnt, it burns completely and produces a higher temperature than air and ethyne. Oxygen and ethyne produce very hot blue flame but the mixture of air and ethyne gives out a sooty flame which means that there are unburnt particles, resulting in lesser heat.
In text questions set 4 Page Number: 74
Question 1
How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid ?
Answer:
Differences between alcohol and carboxylic acid
| Test | Alcohol | Carboxylic acid |
| (i) Litmus test | No change in colour. | Blue litmus solution turns red. |
| (ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test | C2H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction No brisk effervescence. | CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. |
| (iii) Alkaline potassium permanganate | On heating, pink colour disappears. | Does not happen so. |
Question 2
What are oxidising agents ?
Answer:
Oxidising agents are those compounds which either removes Hydrogen or adds oxygen to a compound. Ex: halogens, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid.
In text questions set 5 Page Number: 76
Question 1
Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent ?
Answer:
It is not possible to check if water is hard by using a detergent because detergents are salts of ammonium or sulphonates of long chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soaps they do not react with calcium and magnesium to distinguish nature of water.
Question 2
People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes ?
Answer:
Agitation is necessary to get clean clothes as agitation aid soap micelles to trap the oil, grease or any other impurities that have to be removed. When they are being beaten or agitated, the particles are removed from the clothes’ surfaces and go into the water, thus cleaning the clothes.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Textbook Chapter Questions
Question 1
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
Question 2
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Answer:
(c) Ketone.
Question 3
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer:
(b) The fuel is not burning completely.
Question 4
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons so that the combining atoms complete their outermost shell.
In CH3Cl : C = 6, H = 1 and Cl = 17 And their electronic configuration is C – 2,4, H – 1 and Cl – 2, 8, 7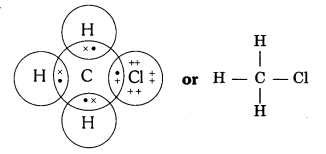
Three hydrogen atoms complete their shells by sharing three electrons (one electron each) of carbon atom.
Chlorine completes its outer shell by sharing its one out of seven electrons with one electron of carbon atom.
Thus carbon atom shares all its four electrons with three hydrogen atoms and one of chlorine atom and completes its outermost shell and single covalent bonds are formed in CH3Cl.
Question 5
Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) propanone
(c) H2S
(d) F2.
Answer: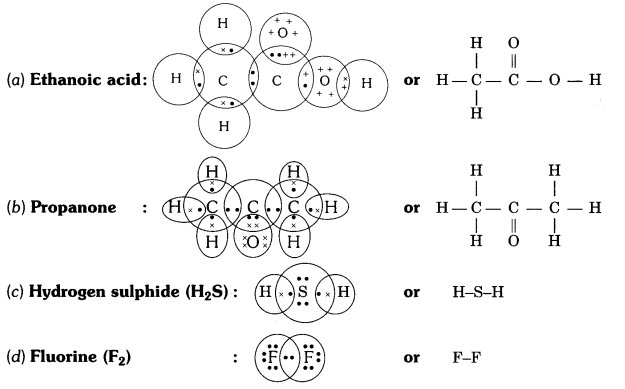
Question 6
What is a homologous series ? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A homologous series is a series of compounds, which has the same functional group. This also contains similar general formula and chemical properties. Since there is a change in the physical properties, we can say that there would be an increase in the molecular size and mass.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2. Methane CH4 Ethane CH3CH3 Propane CH3CH2CH3 Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3. It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
| Value of n | Molecular formula | Name of compound |
| 1 | CH4 | Methane |
| 2 | C2H6 | Ethane |
| 3 | C3H8 | Propane |
| 4 | C4H10 | Butane |
| 5 | C5H12 | Pentane |
Question 7
How can ethanol and ethanoic acid he differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties ?
Answer:
Difference on the basis of physical properties
| Property | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) State | Liquid | Liquid |
| (ii) Odour | Sweet smell | Pungent vinegar-like smell |
| (iii) Melting point | 156 K | 290 K |
| (iv) Boiling point | 351 K | 391 K |
Difference on the basis of chemical properties
| Test | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) Litmus test | No change in the colour of litmus solution. | Blue litmus solution turns red. |
| (ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test | C2H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction No brisk effervescence. | CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. |
| (iii) Alkaline potassium permanganate | On heating, pink colour disappears. | Does not happen so. |
Question 8
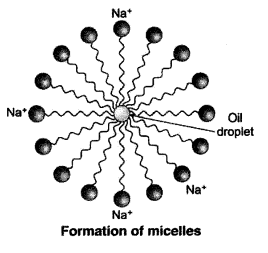
Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water ? Will a micell be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also ?
Answer:
Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water because the hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are hydrophobic (water repelling) which are insoluble in water, but the ionic ends of soap molecules are hydrophilic (water attracting) and hence soluble in water.
Such micelle formation will not be possible in other solvents like ethanol in which sodium salt of fatty acids do not dissolve.
Question 9
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications ?
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds give a large amount of heat per unit weight and are therefore, used as fuels for most applications.
Question 10
Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer:
Scrum is produced from reaction of hard water with soap. Calcium and magnesium present in the hard water form an insoluble precipitate that stick as a white which is also called as scrum.
Question 11
What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer:
When soap is dissolved in water, due to the formation of alkaline NaOH or KOH, the solution is alkaline. The solution changes the colour of the red litmus to blue, but in the soap solution, the blue litmus remains blue.
Question 12
What is hydrogenation ? What is its industrial application ?
Answer:
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydro-carbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place in the presence of nickel (Ni) or palladium (Pd) metals as catalyst.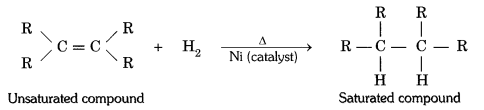
Application : The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) from vegetable oils.
Question 13
Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions :
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4
Answer:
Addition reactions take place only in unsaturated hydrocarbons. So addition reaction take place only in C3H6and C2H2.
Question 14
Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Answer:
Butter is a saturated carbon compound while cooking oil is an unsaturated carbon compound. An unsaturated compound decolourises bromine water, while a saturated compound cannot decolourise it. So we can distinguish chemically between a cooking oil and butter by the bromine water. Add bromine water to a little of cooking oil and butter taken in separate test-tubes.
- Cooking oil decolourises bromine water showing that it is an unsaturated compound.
- Butter does not decolourise bromine water showing that it is a saturated compound.
Question 15
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
OR
Explain the cleansing action of soaps. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer:
There are so many impurities and dirt mixed in water, and most of all the dirt does not dissolve in the water. Soap molecules are a combination of salts such as sodium or potassium. The molecules are of a long chain of carboxylic acids. So, when the carbon chain is dissolved in oil and the ionic end is dissolved in the water, the soap starts cleansing and trapping the dirt. When this happens, the soap molecules form structures that are called micelles are used for capturing the oil droplets and then the other end being the ionic faces. This will then form an emulsion in water and help in dissolving the dirt or impurities when the clothes are washed.
The soap molecules have different properties at different ends. The first end being the hydrophilic end which dissolves in the water and is attracted towards the water and the second one being the hydrophobic end is dissolved in the hydrocarbons and is repulsive to water. The hydrophobic tail aligns itself along the surface of the water because it is not soluble in the water.