NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Updated for 2022-23
NCERT Solution Class 10 Science chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals is about various elements that can be classified as metals or non-metals on the basis of their properties. Students who are preparing for their Class 10 exams and searching for chapter-wise NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science must go through NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals.
ALSO CHECK – NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 is prepared by our best subject experts teachers group thats help students to understand all the topics easily. With the help of these NCERT Solutions for Science, students can understand the complex topics of class 10 science. We all know Science is a subject that needs a clear understanding of the concepts and topics to score well in it.
ALSO READ – Top 5 best laptop under 50000 for students and office uses in India 2022
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals – In-text questions set 1
Page number 40
Question 1
Give an example of a metal which :
(i) is a liquid at room temperature.
(ii) can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) is the best conductor of heat.
(iv) is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
(i) Mercury is the metal which is liquid at room temperature
(ii) Sodium and potassium are the metals which can be cut with a knife
(iii) Silver is the best conductor of heat
(iv) Mercury and lead are poor conductor of heat.
Question 2
Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Malleable : A metal that can be beaten into thin sheets on hammering is called malleable.
Ductile : A metal which can be drawn into thin wires is called ductile.
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 46
Question 1
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil ?
Answer:
Sodium is a reactive metals, if kept open it will react with oxygen to explore and catch fire. Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
Question 2
Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with steam.
(ii) calcium and potassium with water.
Answer: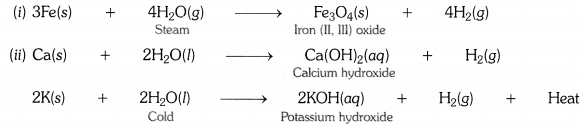
Question 3
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one.
The results obtained have been tabulated as follows :
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(i) Which is the most reactive metal ?
(ii) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
(i) B is the most reactive metal because it gives displacement reaction with iron (II) sulphate.
(ii) When metal B is added to copper (II) sulphate solution, a displacement reaction will take place due to which the blue colour of copper (II) sulphate solution will fade and a red-brown deposit of copper will be formed on metal B.
(iii) Metal B is the most reactive because it displaces iron from its salt solution. Metal A is less reactive because it displaces copper from its salt solution. Metal C is still less reactive because it can displace only silver from its salt solution and metal D is the least reactive because it cannot displace any metal from its salt solution. Hence, the decreasing order of reactivity of the metals is B > A > C > D.
Question 4
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal ? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal.
Chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4 :
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Question 5
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate ? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate, then the greenish colour of iron (II) sulphate solution fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and iron metal is deposited on zinc.
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 49
Question 1
(i) Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer: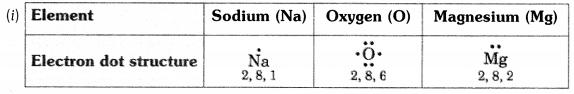
(ii) Formation of Na2O and MgO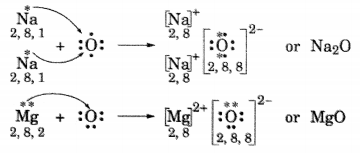
(iii) In Na2O, ions present are Na+ and O2-.
In MgO, ions present are Mg2+ and O2-.
Question 2
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points ?
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer:
The ionic compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compound. Due to this, ionic compounds have high melting points.
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 53
Question 1
Define the following terms : (i) Mineral, (ii) Ore and (iii) Gangue.
Answer:
(i) Mineral : The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals.
(ii) Ore : Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(iii) Gangue : The unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earth particles, lime stone, mica, etc in an ore are called gangue.
Question 2
Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer:
Gold and platinum
Question 3
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
Answer:
Reduction process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
For example, zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc by heating with carbon.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Besides carbon, highly reactive metals like sodium, calcium, aluminium etc. are used as reducing agents. These displace metals of low reactivity from their oxides.
For example,
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Gold is Metal or Nonmetal ?
Gold is a metal found in nature in the free state
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 55
Question 1
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | |||
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | |||
| 3. | Copper oxide |
In which cases will you find displacement reactions taking place ?
Answer:
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide. But out of zinc, magnesium, and copper metals, magnesium is the most reactive, zinc is less reactive whereas copper is the least reactive metal.
The displacement will take place in the following cases :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | – | Displacement | – |
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | – | – | – |
| 3. | Copper oxide | Displacement | Displacement | – |
Question 2
Which metals do not corrode easily ?
Answer:
Gold and Platinum.
Question 3
What are alloys ?
Answer:
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. For example, bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Textbook Chapter End Questions – Page number 56-57
Question 1.
Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions ?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal.
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal.
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal.
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Answer:
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Question 2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting ?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint.
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) Applying a coating of zinc.
Question 3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer:
(a) Calcium.
Question 4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
(c) zinc is less reactive than tin
(d) zinc is more reactive than tin.
Answer:
(d) Zinc is more reactive than tin.
Question 5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Answer:
(a) Metals can be beaten into thin sheets with a hammer without breaking. Non-metals cannot be beaten with a hammer to form thin sheets. Non-metals break into pieces when hammered. Metals are malleable, while non-metals are non-melleable. When metals are connected into circuit using a battery, bulb, wires and switch, current passes through the circuit and the bulb glows. When non-metals (like sulphur) are connected, the bulb does not light up at all. Metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) Because of malleability, metals can be casted into sheets. Metals are good conductors of electricity so these can be used for electrical cables.
Question 6.
What are amphoteric oxides ? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides ?
OR
Write chemical equations that show aluminium oxide reacts with acid as well as base. [CBSE2011]
Answer:
Those metal oxides which show basic as well as acidic behaviour are known as amphoteric oxides. In other words, metal oxides that react wtih both acids and bases to form salt and water are called amphoteric oxides. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature.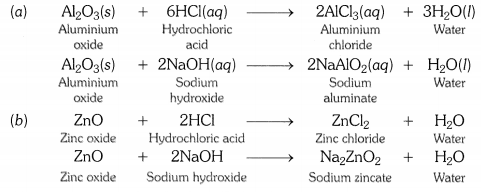
Question 7.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not.
Answer:
(i) Metals above hydrogen in the activity series like sodium and magnesium displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
(ii) Metals below hydrogen in the activity series like copper, silver do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 8.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte ?
Answer:
Cathode – Pure metal
Anode – Impure metal
Electrolyte – Metal salt solution
Question 9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in the figure.
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper ?
(ii) moist litmus paper ?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.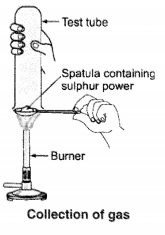
Answer:
(i) Dry litmus paper – no action.
(ii) Moist litmus paper – becomes red.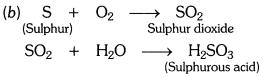
Question 10.
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
Ways to prevent rusting of iron are :
(a) By painting
(b) By galvanizing
Question 11.
What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen ?
Answer:
Non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.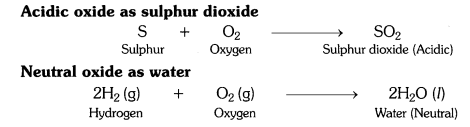
Question 12.
Give reasons :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery because these are malleable and ductile. These are highly resistant to corrosion.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are very reactive and catch fire when exposed to air. This is due to their low ignition temperature and high reactivity.
(c) Aluminium forms a non-reactive layer of aluminium oxide on its surface. This layer prevents aluminium to react with other substances. That’s why aluminium is used to make cooking utensils.
(d) It is easier to reduce a metal oxide into free metal. Since it is easier to obtain metals from their oxides than from their carbonates or sulphides directly, therefore, the carbonate and sulphide ores are first converted to oxides for extracting the metals.
Question 13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Answer:
The sour substances such as lemon or tamarind juice contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and makes them shining red-brown again.
Question 14.
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties. [CBSE 2017 (Delhi)]
Answer:
Difference between metals and non-metals
| Metals | Non-metals |
| (i) Metals form basic oxides or amphoteric oxides. | (i) Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| (ii) Metals replace hydrogen from acids and form salts. | (ii) Non-metals do not replace hydrogen from acids. |
| (iii) With chlorine, metals form chlorides which are electrovalent. | (iii) With chlorine, non-metals form chlorides which are covalent. |
| (iv) With hydrogen few metals form hydrides which are electrovalent. | (iv) With hydrogen, non-metals form many stable hydrides which are covalent. |
Question 15.
A man went door-to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty repeat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he has used ?
Answer:
The dishonest goldsmith dipped the gold bangles in aqua-regia (which contains 1 part of concentrated nitric acid and 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid, by volume). Aqua-regia dissolved a considerable amount of gold from gold bangles and hence reduced their weight drastically. The dishonest goldsmith can recover the dissolved gold from aqua-regia by a suitable treatment.
Question 16.
Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (analloy of iron).
Answer:
(i) Copper is a better conductor of heat than steel.
(ii) Copper does not corrode easily. But steel corrodes easily.
(iii) Copper does not react with water at any temperature, whereas iron reacts with water on heating.







