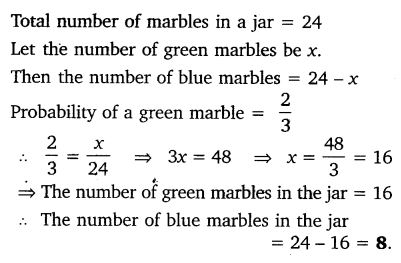NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Exercise 15 are prepared by specialised experienced mathematic teacher. Maths are most important subject of board and with the help of this chapter-wise NCERT solution and little practices you can get very good marks in your respective board exam. It also help students to build a foundation of upcoming class 11th and 12th. Student can also check the Important Question with solution for class 9 to class 12.
Also Check – To known more about latest Mobile, Laptop and other gadget click here
Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Exercise 15 contain total 2 exercise that has 30 questions and questions based on based on the concept of theoretical probability. Check Previous chapter – NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics Exercise 14
Important Formulas –
- The theoretical probability (also called classical probability) of an event E, written as P(E), is defined as
Let n be the total number of trails. The empirical probability of an event E happening, is given by
![]()
(i) Experiment : An operation which can produce some well defined outcomes is known as experiment.
(ii) Trail : Performing of an experiment is called trial.
(iii) Equally likely outcomes : Outcomes of trial are equally likely if there is no reason to accept one in preference to the others.
(iv) Sample space : The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called sample space.
(v) Elementary event : An event having only one outcome
Note that the sum of probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is 1.
Probability – A Theoretical Approach(Classical Probability)
If an event ‘A’ can happen is ‘m’ ways and does not happen in ‘n’ ways, then the probability of occurrence of event ‘A’ denoted by P(A) is given by
Number of favourable outcomes m

Probability of Impossible and Sure Events
The probability of an event which is impossible to occur is 0 and such an event is called impossible event, i.e; for impossible event T, P(I) = 0
The probability of an event which is sure or certain to occur is 1 and such an event is called sure event or certain event.
i.e; for sure event or certain event ‘s’, P(s) = 1
Exercise 15.1
Question 1.
Complete the following statements:
(i) Probability of an event E + Probability of the event ‘not E’ = ………
(ii) The probability of an event that cannot happen is ……… Such an event is called ………
(iii) The probability of an event that is certain to happen is ………. Such an event is called ………
(iv) The sum of the probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is ………..
(v) The probability of an event is greater than or equal to …………. and less than or equal to ………..
Solution:

Question 2.
Which of the following experiments have equally likely outcomes? Explain.
(i) A driver attempts to start a car. The car starts or does not start.
(ii) A player attempts to shoot a basketball. She/he shoots or misses the shot.
(iii) A trial is made to answer a true-false question. The answer is right or wrong.
(iv) A baby is born. It is a boy or a girl.
Solution:

Question 3.
Why is tossing a coin considered to be a fair way of deciding which team should get the bail at the beginning of a football game?
Solution:
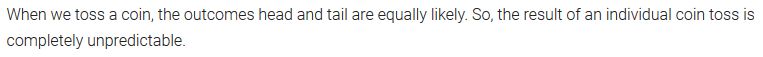
Question 4.
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(A) 23
(B) -1.5
(C) 15%
(D) 0.7
Solution:
![]()
Ex 15.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
If P (E) = 0.05, what is the probability of ‘not E’?
Solution:
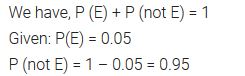
Question 6.
A bag contains lemon flavoured candies only. Malini takes out one candy without looking into the bag. What is the probability that she takes out
(i) an orange flavoured candy?
(ii) a lemon flavoured candy?
Solution:

Question 7.
It is given that in a group of 3 students, the probability of 2 students not having the same birthday is 0.992. What is the probability that the 2 students have the same birthday?
Solution:
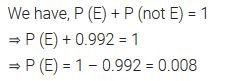
Question 8.
A bag contains 3 red balls and 5 black balls. A ball is drawn at random from the bag. What is the probability that the ball drawn is
(i) red?
(ii) not red?
Solution:
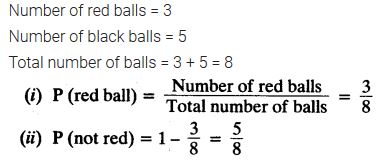
Question 9.
A box contains 5 red marbles, 8 white marbles and 4 green marbles. One marble is taken out of the box at random. What is the probability that the marble taken out will be
(i) red?
(ii) white?
(iii) not green?
Solution:
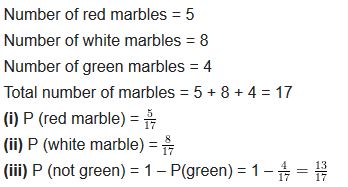
Question 10.
A piggy bank contains hundred 50 p coins, fifty ₹ 1 coins, twenty ₹ 2 coins and ten ₹ 5 coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall out when the bank is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin
(i) will be a 50 p coin?
(ii) will not be a ₹ 5 coin?
Solution:

Question 11.
Gopi buys a fish from a shop for his aquarium. The shopkeeper takes out one fish at random from a tank containing 5 male fish and 8 female fish (see figure). What is the probability that the fish taken out is a male fish?

Solution:
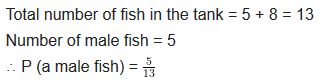
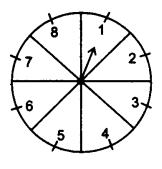
Question 12.
A game of chance consists of spinning an arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 (see figure.), and these are equally likely outcomes. What is the probability that it will point at
(i) 8?
(ii) an odd number?
(iii) a number greater than 2?
(iv) a number less than 9?
Solution:
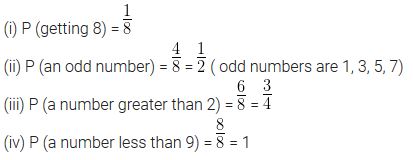
Question 13.
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting
(i) a prime number
(ii) a number lying between 2 and 6
(ill) an odd number
Solution:

Question 14.
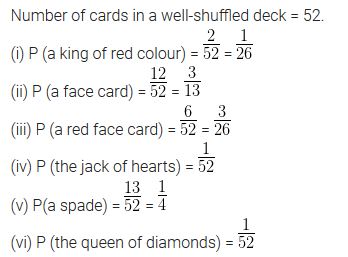
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting
(i) a king of red colour
(ii) a face card
(iii) a red face card
(iv) the jack of hearts
(v) a spade
(vi) the queen of diamonds
Solution:
Question 15.
Five cards – the ten, jack, queen, king and ace of diamonds, are well shuffled with their face downwards. One card is then picked up at random.
(i) What is the probability that the card is the queen?
(ii) If the queen is drawn and put aside, what is the probability that the second card picked up is
(a) an ace?
(b) a queen?
Solution:

Question 16.
12 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 132 good ones. It is not possible to just look at a pen and tell whether or not it is defective. One pen is taken out at random from this lot. Determine the probability that the pen taken out is a good one.
Solution:

Question 17.
(i) A lot of 20 bulbs contain 4 defective ones. One bulb is drawn at random from the lot. What is the probability that this bulb is defective?
(ii) Suppose the bulb drawn in (i) is not defective and is not replaced. Now one bulb is drawn at random from the rest. What is the probability that this bulb is not defective?
Solution:

Question 18.
A box contains 90 discs which are numbered from 1 to 90. If one disc is drawn at random from the box, find the probability that it bears
(i) a two digit number.
(ii) a perfect square number.
(iii) a number divisible by 5.
Solution:

Question 19.
A child has a die whose six faces show the letters as given below:
![]()
The die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting
(i) A?
(ii) D?
Solution:

Question 20.
Suppose you drop a die at random on the rectangular region shown in figure. What is the probability that it will land inside the circle with diameter 1 m?
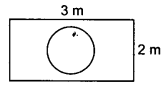
Solution:

Question 21.
A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 are defective and the others are good. Nuri will buy a pen if it is good, but will not buy if it is defective. The shopkeeper draws one pen at random and gives it to her. What is the probability that
(i) she will buy it?
(ii) she will not buy it?
Solution:

Question 22.
Two dice, one blue and one grey, are thrown at the same time. Now
(i) Complete the following table:
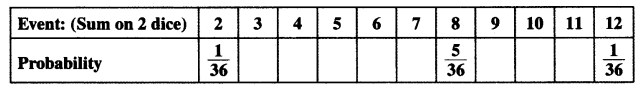
(ii) A student argues that-there are 11 possible outcomes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Therefore, each of them has a probability 111. Do you agree with this argument? Justify your answer.
Solution:

Question 23.
A game consists of tossing a one rupee coin 3 times and noting its outcome each time. Hanif wins if all the tosses give the same result, i.e. three heads or three tails, and loses otherwise. Calculate the probability that Hanif will lose the game.
Solution:

Question 24.
A die is thrown twice. What is the probability that
(i) 5 will not come up either time?
(ii) 5 will come up at least once?
[Hint: Throwing a die twice and throwing two dice simultaneously are treated as the same experiment.]
Solution:

Question 25.
Which of the following arguments are correct and which are not correct? Give reasons for your answer.
(i) If two coins are tossed simultaneously there are three possible outcomes- two heads, two tails or one of each. Therefore, for each of these outcomes, the probability is 13.
(ii) If a die is thrown, there are two possible outcomes- an odd number or an even number. Therefore, the probability of getting an odd number is 12.
Solution:

Exercise 15.2
Question 1.
Two customers Shyam and Ekta are visiting a particular shop in the same week (Tuesday to Saturday). Each is equally likely to visit the shop on any day as on another day. What is the probability that both will visit the shop on
(i) the same day?
(ii) consecutive days?
(iii) different days?
Solution:


Question 2.
A die is numbered in such a way that its faces show the number 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 6. It is thrown two times and the total score in two throws is noted. Complete the following table which gives a few values of the total score on the two throws:
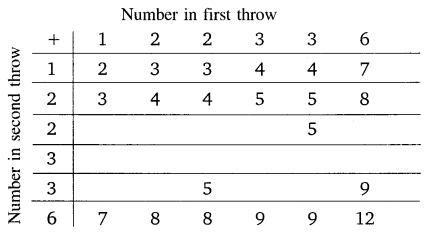
What is the probability that the total score is at least 6?
(i) even
(ii) 6
(iii) at least 6
Solution:

Question 3.
A bag contains 5 red balls and some blue balls. If the probability of drawing a blue ball is doubles that of a red ball, determine the number of blue balls in the bag.
Solution:
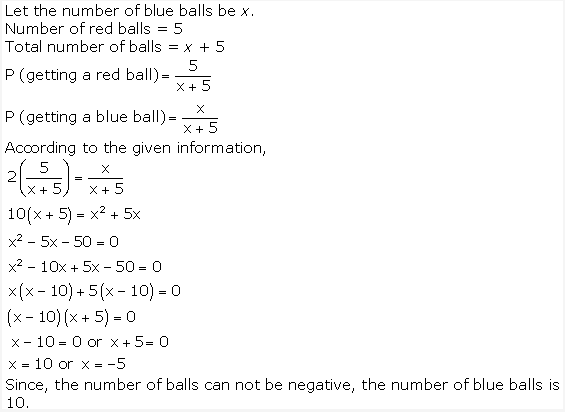
Question 4.
A box contains 12 balls out of which x are black. If one ball is drawn at random from the box, what is the probability that it will be a black ball? If 6 more black balls are put in the box, the probability of drawing a black ball is now double of what it was before. Find x.
Solution:

Question 5.
A jar contains 24 marbles, some are green and others are blue. If a marble is drawn at random from the jar, the probability that it is green is 2/3. Find the number of blue balls in the jar.
Solution: